Which of the Following Statements About Neisseria Meningitis Is False
Doctors call meningitis caused by the bacteria Neisseria meningitidis meningococcal meningitis. Bacteria called Neisseria meningitidis cause meningococcal disease.

C Reactive Protein Is Useful In Distinguishing Gram Stain Negative Bacterial Meningitis From Viral Meningitis In Children The Journal Of Pediatrics
Haemophilus influenzae type b.

. 4 Which of the following statements about Neisseria meningitis is FALSE. D Transmission is via respiratory droplets. Neisseria species may be misidentified as N.
Complement component 8 deficiency is caused by mutations in the C8A or C8B gene. Many aspects of bacterial colonization cell invasion and immune evasion have. Here we report a case of false-negative results for real-time PCR for a Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B isolate with a polymorphism in the ctrA gene.
About 1 in 10 people have these bacteria in the back of their nose and throat without being ill. Therefore another test should be performed if the following conditions occur. Other symptoms may include nausea vomiting increased sensitivity to light and confusion.
Common symptoms of meningococcal meningitis include sudden fever headache and stiff neck. The isolates suspected of being gonococci do not. Both false-positive results cross-reactions with other Neisseria species such as Neisseria meningitidis Neisseria lactamica N cinerea and K denitrificans and false-negative results have been reported for the coagglutination tests 1012-14.
C8A gene mutations underlie type I and C8B gene mutations cause type II. Meningitidis does not produce polysaccharide from sucrose. Despite advances that have contributed to our understanding of disease pathogenesis Neisseria meningitidis Nm remains an important cause of morbidity and mortality globallyThe genomes of 1000 isolates of Nm have been sequenced and are available to the public.
Children and infants may show different signs and symptoms such as inactivity. False penicillin resistance in Neisseria meningitidis following direct susceptibility tests from blood cultures N C Weightman Abstract Blood cultures drawn from a patient with clinically diagnosed invasive meningococ-cal disease who had been previously administered benzylpenicillin had â-lactamases added to increase the prob-. Meningitidis can be classified into 12 serogroups based on its capsular polysaccharide.
However sometimes the result is a false negative and despite the negative culture result other signs and laboratory tests strongly indicate that the child likely has bacterial meningitis. People in the same household. C It is typically transmitted by droplet aerosols or direct contact with secretions.
A There are vaccines available to prevent infection with all strains. A It is encapsulated. D A healthy carrier state can exist.
This complex is composed of an alpha subunit produced from the C8A gene a beta subunit. Bacterial meningitis caused by the bacteria Neisseria meningitidis also called meningococcal meningitis is the most important example. Meningitidis in acid detection tests.
Which of the following organisms causes epidemic meningitis cases at college campuses. Which of the following statements about Neisseria meningitidis is FALSE. When someone has meningococcal meningitis the bacteria infect the lining of the.
B Up to 40 of the population are carriers. Viral meningitis is spread through contaminated saliva respiratory tract secretions and respiratory droplets thereby requiring droplet isolation. B Its most distinguishing feature is a unique rash.
The two most common types of meningococcal infections are meningitis and septicemia. Serogroups A B C W X and Y are the primary causes of meningococcal disease worldwide. It normally colonizes the upper respiratory tract of some people.
The conjugate vaccine against serogroup A Neisseria meningitidis NmA MenAfriVac is currently being introduced throughout the African meningitis belt. The symptoms of meningococcal disease can vary based on the type of illness. Meningococcal disease is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis.
Yes some forms of bacterial meningitis are especially contagious. This is called being a carrier Sometimes the bacteria invade the body and cause certain illnesses which are known as meningococcal disease. Etiological diagnosis then mainly relies on PCR.
Both of these types of infections are very serious and can be deadly in a matter of hours. Which of the following statements regarding Neisseria meningitidis is FALSE. Which of the following is the most common cause of neonatal meningitis.
Although strains of some organisms do not grow on medium on which polysaccharide is detected polysaccharide may be detected in the growth inoculated onto the plate. PCR is a rapid test and has high sensitivity and specificity. Viral meningitis is a rare form of meningitis and is caused by inhalation of fungal spores.
C Humans are the only natural carriers. In repeated multicentre cross-sectional studies in Burkina Faso we demonstrated a significant effect of vaccination on NmA carriage for one year following mass vaccination in 2010. Early treatment of meningococcal meningitis is mandatory but may negate the cerebrospinal fluid culture.
1 and 4 are true for bacterial meningitis. E It often causes meningitis. It can infect the.
A major advantage of PCR is that it allows for detection of Hi and Nm from clinical samples in which the organism cannot be detected by culture methods such as when a patient has been treated with antibiotics before a clinical specimen is obtained for culture. The overall rates have been declining 1 2 since the introduction of vaccines against the three most common meningeal pathogens Haemophilus influenzae type b Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitides and by the introduction of. These genes provide instructions for making pieces of a protein complex called complement component 8.
3 is true for fungal meningitis. Acute bacterial meningitis ABM is a life-threatening bacterial infection of the meninges. The bacteria are spread through the exchange of respiratory and throat secretions such as coughing for example.
The most common cause of a false-negative bacterial culture result is that the child received antibiotics before the test was done.

11k Likes 53 Comments Ron Ronwritings On Instagram False Hopes Reality Quotes Instagram Quotes Favorite Quotes
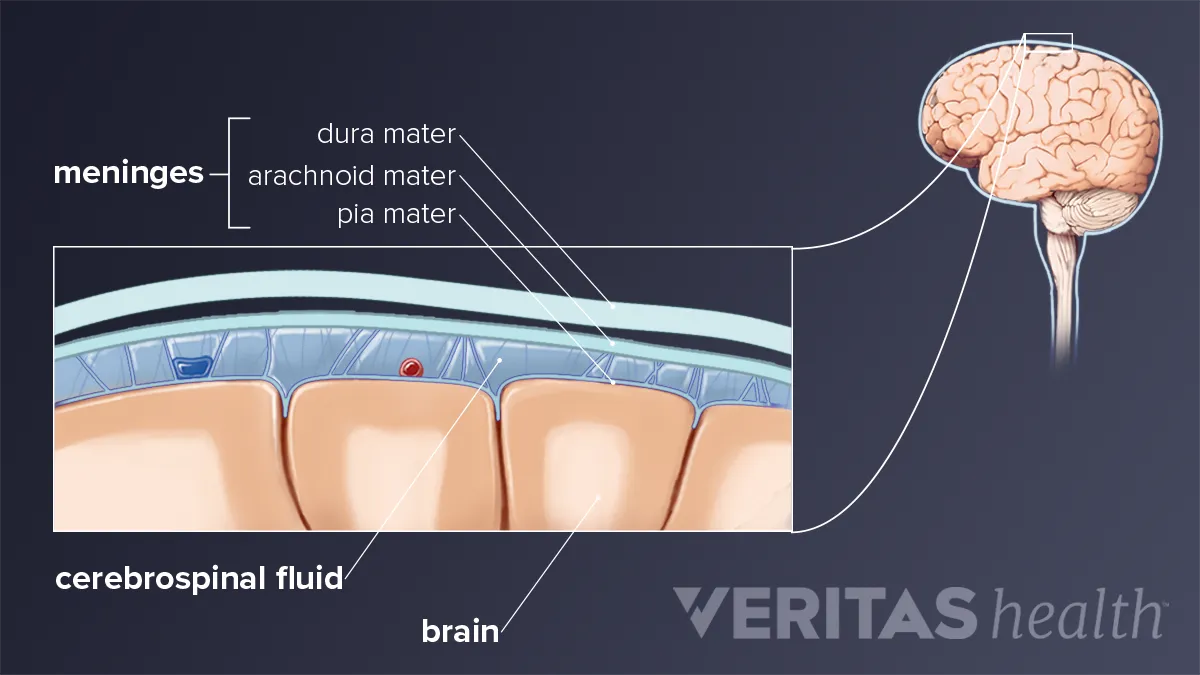
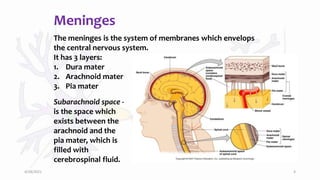
How Meningitis Causes Neck Pain And Stiffness

Meningitis Quiz Faqs Frequently Asked Questions Rxlist

Meningitis Bacteria Meningitis Bacteria Macro And Micro

Community Acquired Bacterial Meningitis The Lancet

Pasteurella Multocida Alexander Mcqueen Scarf Memento Mori Mcqueen
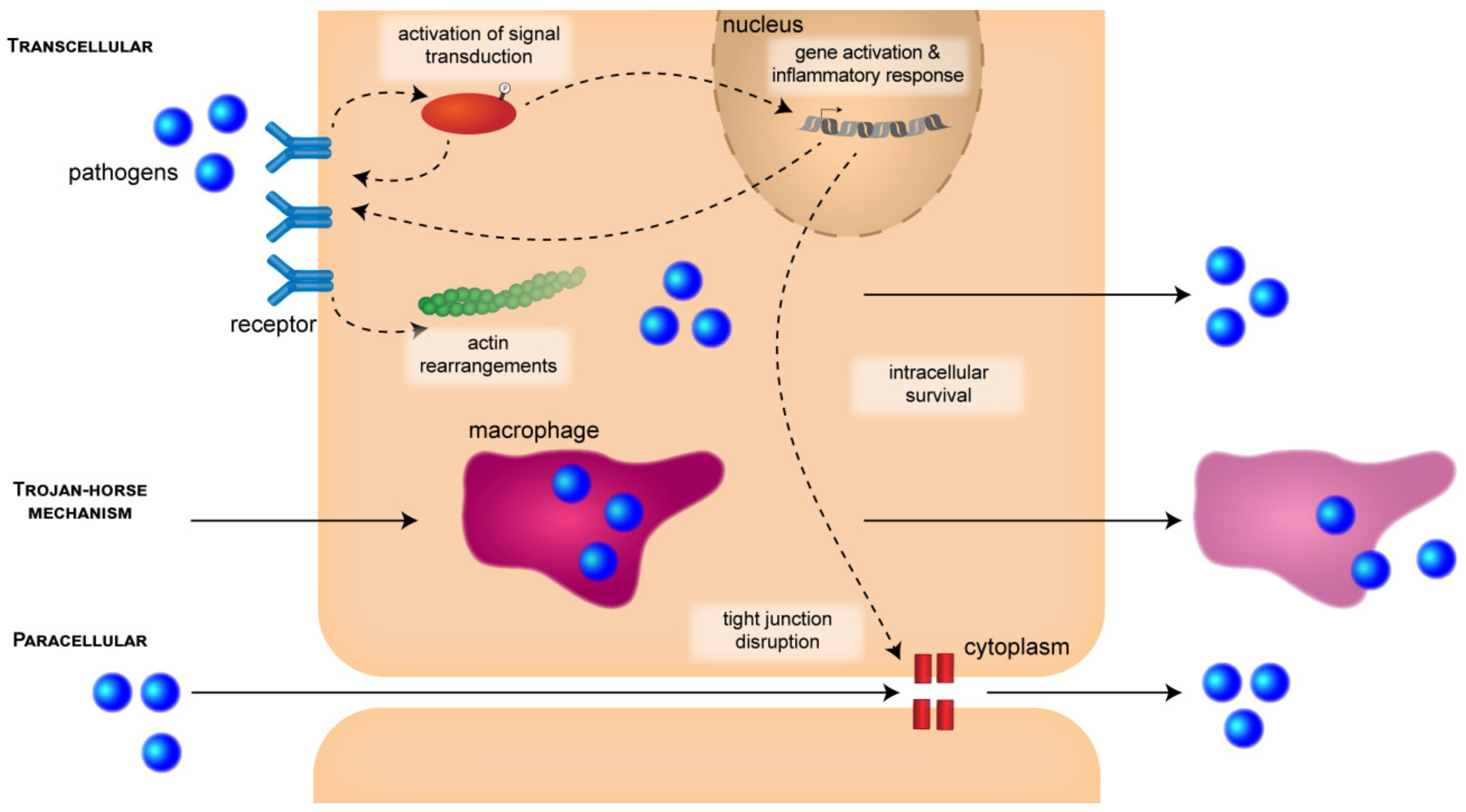
Ijms Free Full Text Virulence Factors Of Meningitis Causing Bacteria Enabling Brain Entry Across The Blood Brain Barrier Html

Lactobacillus Bulgaricus In Yogurt 2 Colonies Lactobacilli Are Probiotic Bacteria They Produce Ba Lactobacillus Bulgaricus Lactobacilli Probiotic Bacteria

Meningitis Bacteria Neisserai Meningitidis Macro And Micro Microbiology Meningitis

Meningitis Bacteria Sem Stock Image C007 4743 Microscopic Photography Scanning Electron Micrograph Meningitis

Penyakit Meningitis Apakah Bisa Dicegah Dan Diobati Iptek Laporan Seputar Sains Dan Teknologi Dan Lingkungan Dw 10 04 2020

Identification Of Neisseria Meningitidis By Maldi Tof Ms May Not Be Reliable Clinical Microbiology And Infection

Applications Of Nanomaterials In Neisseria Meningitidis Infection Sciencedirect

Meningitis Introduction Openwho

Applications Of Nanomaterials In Neisseria Meningitidis Infection Sciencedirect


Comments
Post a Comment